Resolvers
Apollo Server 需要知道如何为 schema 中的每个字段填充数据,以让它可以响应查询数据的请求。为了实现这一点,它使用 resolver。
resolver 是一个负责给 schema 中单个字段填充数据的函数。它可以填充以任何方式定义的数据,例如查询后端数据库或者第三方 API。
如果不为特定字段定义 resolver,Apollo Server 将为这个字段定义一个default resolver。
定义 resolver
基础语法
假设我们服务器定义了以下(非常简短)的 schema:
type Query {
numberSix: Int! # Should always return the number 6 when queried
numberSeven: Int! # Should always return 7
}
我们想要给根Query类型的numberSix和numberSeven字段定义 resolver,以让它们在需要的时候,永远返回6和7。
这些 resolver 的定义大概如下:
const resolvers = {
Query: {
numberSix() {
return 6;
},
numberSeven() {
return 7;
},
},
};
如例子所示:
- 服务器上所有的 resolver 被定义在一个单独的 JavaScript 对象中(前面示例中被命名为
resolvers)。这个对象被称作resolver map。 - resolver map 拥有与 schema 的类型(如前面示例中的
Query)相对应的顶级字段。 - 每一个 resolver 函数都属于对应字段所属的类型。
私货:resolver 和 resolver map,不是一个概念。
resolver->field
resolver map->top-level type(更偏向 schema 整体的层级)
传递参数
假设我们定义了如下的 schema:
type User {
id: ID!
name: String
}
type Query {
user(id: ID!): User
}
我们希望能够通过 user 的id来查询user字段,以获取 user 对应的信息。
为了达到这个目的,我们的服务器需要访问 user 数据。针对这个认为的例子,假设我们的服务器定义了如下硬编码的数组:
const users = [
{
id: "1",
name: "Elizabeth Bennet",
},
{
id: "2",
name: "Fitzwilliam Darcy",
},
];
现在我们可以给user字段定义 resolver,像下面这样:
const resolvers = {
Query: {
user(parent, args, contextValue, info) {
return users.find((user) => user.id === args.id);
},
},
};
如例子所示:
resolver 可以选择接收四个参数:
(parent, args, contextValue, info)- 更多细节,参考arguments
args参数是一个对象,它包含了通过 GraphQL operation 提供给字段的所有 GraphQL 参数。
注意,这个例子没有给
User字段(id和name)定义 resolver。是因为 Apollo Server 为这些字段创建的 default resolver 做了正确的事:它直接从对象获取值并通过userresolver 返回。
将 resolver map 传递给 Apollo Server
在下面的例子中,我们使用顶层
await来异步起动我们的服务器。如果你想了解如何配置,请查看 Getting Started 获取更多详细信息。
在定义了所有 resolver 之后,搭配着 schema 的定义(作为typeDefs属性)一起,将它们(作为resolvers属性)传递给Apollo Server的构造函数。
下面的例子定义了硬编码的数据集、schema 和 resolver map。在将 schema 和 resolver map 传递给Apollo Server后初始化了实例。
import { ApolloServer } from "@apollo/server";
import { startStandaloneServer } from "@apollo/server/standalone";
// Hardcoded data store
const books = [
{
title: "The Awakening",
author: "Kate Chopin",
},
{
title: "City of Glass",
author: "Paul Auster",
},
];
// Schema definition
const typeDefs = `#graphql
type Book {
title: String
author: String
}
type Query {
books: [Book]
}
`;
// Resolver map
const resolvers = {
Query: {
books() {
return books;
},
},
};
// Pass schema definition and resolvers to the
// ApolloServer constructor
const server = new ApolloServer({
typeDefs,
resolvers,
});
// Launch the server
const { url } = await startStandaloneServer(server);
console.log(`🚀 Server listening at: ${url}`);
注意,你可以在多个文件和对象中定义 resolver,只要将所有 resolver 合并到一个单独的、被传递给ApolloServer构造函数的 resolver map 即可。
Resolver chain
当 query 请求一个返回值为对象类型的字段时,这个 query 至少也要访问该对象(如果没有查询该对象中的字段,没有理由在 query 中包含这个对象)字段中的一个。一个 query 最底层的字段,永远返回 scalar、enum 或者它们的列表。
私货:bottom out,最底层?我好像明白了,但是嘴说不出来 🤣
举个例子,Product类型的所有字段都属于“bottom out”:
type Product {
id: ID!
name: String
variants: [String!]
availability: Availability!
}
enum Availability {
AVAILABLE
DISCONTINUED
}
由于这个规则,Apollo Server 解析一个返回值为对象类型的字段时,它永远会解析这个对象的一个或更多字段。那些子字段或许也包含对象类型。根据 schema,object-field 模式可以持续到任意深度,这个过程被称为 resolver chain。
例子
假设服务器定义了如下的 schema:
# A library has a branch and books
type Library {
branch: String!
books: [Book!]
}
# A book has a title and author
type Book {
title: String!
author: Author!
}
# An author has a name
type Author {
name: String!
}
type Query {
libraries: [Library]
}
下面是一个针对该 schema 有效的 query:
query GetBooksByLibrary {
libraries {
books {
author {
name
}
}
}
}
这个 query 的 resolver chain 查询过程,符合 query 本身的层级结构:

这些 resolver 按前面所示的顺序执行,并且它们各自的返回值都会通过parent参数传递给下一个处于 resolver chain 中的 resolver。
这里有一段代码示例,它可以用这个 resolver chain 解析前面的 query:
import { ApolloServer } from "@apollo/server";
import { startStandaloneServer } from "@apollo/server/standalone";
const libraries = [
{
branch: "downtown",
},
{
branch: "riverside",
},
];
// The branch field of a book indicates which library has it in stock
const books = [
{
title: "The Awakening",
author: "Kate Chopin",
branch: "riverside",
},
{
title: "City of Glass",
author: "Paul Auster",
branch: "downtown",
},
];
// Schema definition
const typeDefs = `#graphql
# A library has a branch and books
type Library {
branch: String!
books: [Book!]
}
# A book has a title and author
type Book {
title: String!
author: Author!
}
# An author has a name
type Author {
name: String!
}
# Queries can fetch a list of libraries
type Query {
libraries: [Library]
}
`;
// Resolver map
const resolvers = {
Query: {
libraries() {
// Return our hardcoded array of libraries
return libraries;
},
},
Library: {
books(parent) {
// Filter the hardcoded array of books to only include
// books that are located at the correct branch
return books.filter((book) => book.branch === parent.branch);
},
},
Book: {
// The parent resolver (Library.books) returns an object with the
// author's name in the "author" field. Return a JSON object containing
// the name, because this field expects an object.
author(parent) {
return {
name: parent.author,
};
},
},
// Because Book.author returns an object with a "name" field,
// Apollo Server's default resolver for Author.name will work.
// We don't need to define one.
};
// Pass schema definition and resolvers to the
// ApolloServer constructor
const server = new ApolloServer({
typeDefs,
resolvers,
});
// Launch the server
const { url } = await startStandaloneServer(server);
console.log(`🚀 Server listening at: ${url}`);
如果更新 query 还去查询每本 book 的title字段:
query GetBooksByLibrary {
libraries {
books {
title
author {
name
}
}
}
}
resolver chain 看起来就是下面的样子了:
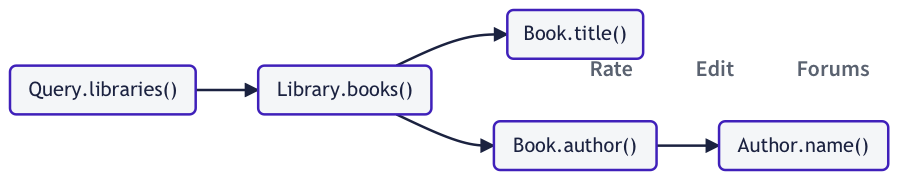
当一个 resolver chain 像这样分叉后,每一个 subchain 都可以并行执行。
Resolver 参数
resolver 函数被传递了 4 种参数:parent、args、contextValue和info(按顺序排列)。
你可以在代码中使用任何名字来命名这些参数,但是 Apollo 文档使用这些名称作为惯例。也常用父类型的名字或
source来替代parent。
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
parent | 这个字段父级 resolver 的返回值(也就是指,resolver chain 中的前一个 resolver)。 对于没有父级的顶级字段的 resolver(例如Query的字段),这个值从传递给 Apollo Server 构造函数的rootValue函数获取。 |
args | 一个包括提供给这个字段全部 GraphQL 参数的对象。举个例子,当执行query{ user(id: "4")}时,被传递给userresolver 的args对象是{ "id": "4"} |
contextValue | 在一个 operation 执行的全部 resolver 中共享的对象。使用这个对象分享给每个 operation 的状态,包括认证信息、dataloader 实例和任何其他跨 resolver 访问的信息。查看contextValue argument以了解更多信息。 |
info | 容纳关于 operation 执行状态的信息,包括字段名称、从根字段到这个字段的路径和更多信息。它的核心字段被列在GraphQL.js 源码。Apollo Server 使用cacheControl字段来完善它。 |
contextValue参数
resolver 永远不应该破坏性地修改
contextValue参数。这确保了所有 resolver 之间的一致性并防止非预期错误的产生。
resolver 通过第三个参数可以访问共享的contextValue对象。为指定 operation 执行的所有 resolver 都可以访问contextValue:
import { UserAPI } from "./datasources/users";
const resolvers = {
Query: {
// Our resolvers can access the fields in contextValue
// from their third argument
currentUser: (_, __, contextValue) => {
return contextValue.dataSources.userApi.findUser(contextValue.token);
},
},
};
interface MyContext {
// Context typing
token?: String;
dataSources: {
userApi: UserAPI;
};
}
const server = new ApolloServer<MyContext>({
typeDefs,
resolvers,
});
const { url } = await startStandaloneServer(server, {
context: async ({ req }) => ({
token: getToken(req.headers.authentication),
dataSources: {
userApi: new UserAPI(),
},
}),
});
了解更多关于管理连接数据库或其他数据源,请参考Fetching Data
更多信息和示例,参考Sharing context。
返回值
resolver 函数的返回值,根据它的类型被 Apollo Server 以不同方式处理。
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| scalar/object | resolver 可以返回一个单独的值或对象,就像在Defining a schema中展示的一样。这个返回值通过parent参数,向下传递给任何嵌套的 resolver。 |
Array | 当且仅当 schema 与 resolver 关联的字段包含一个列表时,才返回一个数组。返回数组后,Apollo Server 对数组中的每一项执行嵌套 resolver。 |
null/undefined | 表明这个字段的值无法被找到。如果 scheme 标明 resolver 的字段可以为 null,那么这个 operation 的结果,在字段的位置会填充null作为返回值。如果 resolver 的字段不能为 null,Apollo Server 设置字段的父级为null。如有必要,这个过程持续向上 resolver chain 知道它到达一个可以为 null 的字段。这确保了返回值永远不会给一个不能为 null 的字段返回null。当出现这种情况时,响应中的errors属性将被填充与字段的是否允许为 null 相关的错误。 |
Promise | resolver 可以异步,而且可以执行异步操作,例如从数据库或后端 API 获取数据。为了支持这些能力,resolver 可以返回 promise,该 promise 解析为任何其他支持的返回类型。 |
Default resolver
如果不为指定的 schema 字段定义 resolver,Apollo Server 会给它定义一个 default resolver。
default resolver 函数的调用逻辑如下:
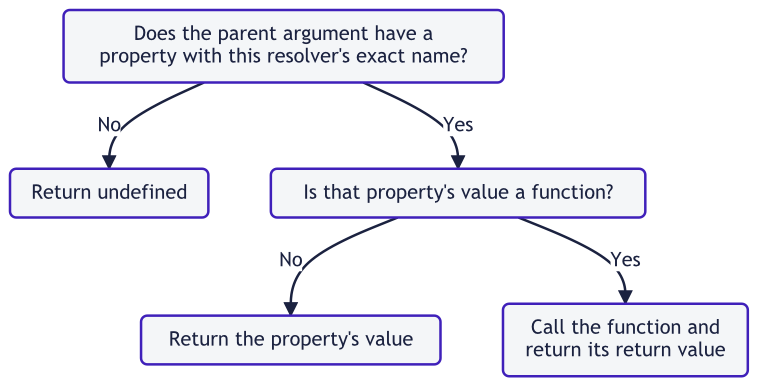
作为一个例子,思考下面 schema 片段:
type Book {
title: String
}
type Author {
books: [Book]
}
如果books字段的 resolver 返回一个对象的数组,每个对象包含title字段,你可以对title字段使用 default resolver。default resolver 将正确返回parent.title。
解析 union 和 interface
这些 GraphQL 类型允许去定义一个返回多种可能对象类型中一种的字段。为了解析可以返回不同对象类型的字段,必须定义__resolveType函数去告知 Apollo Server 哪个对象的类型将被返回。
解析 federated entities
监控 resolver 性能
与所有代码一样,resolver 的性能取决于它的逻辑。最重要的是理解哪些 schema 字段是计算成本高或解析缓慢,这样才能提升它们的性能或确保只在必要的时候查询这些字段。
Apollo Studio 直接集成 Apollo Server,以提供顶层字段的监控指标,这可以帮助及时了解 graph 的性能。更多信息,参考Analyzing performance